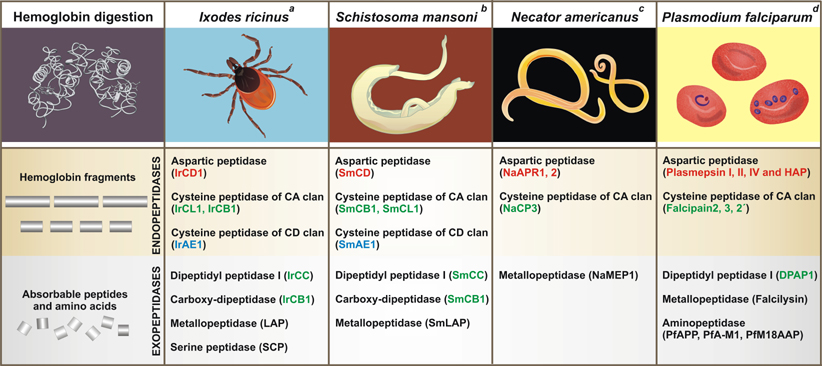
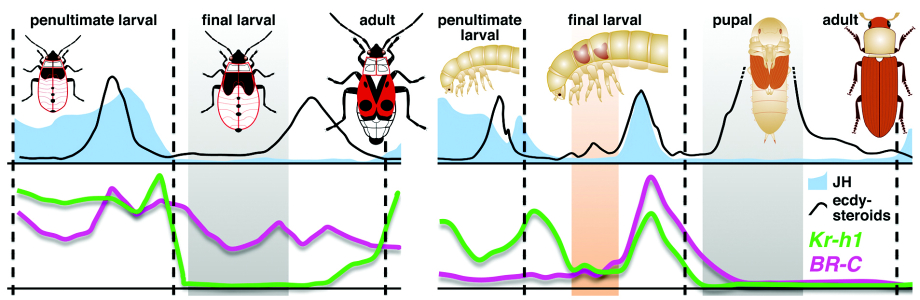
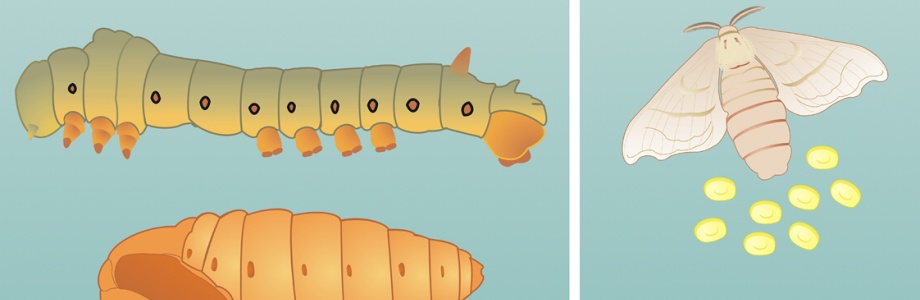
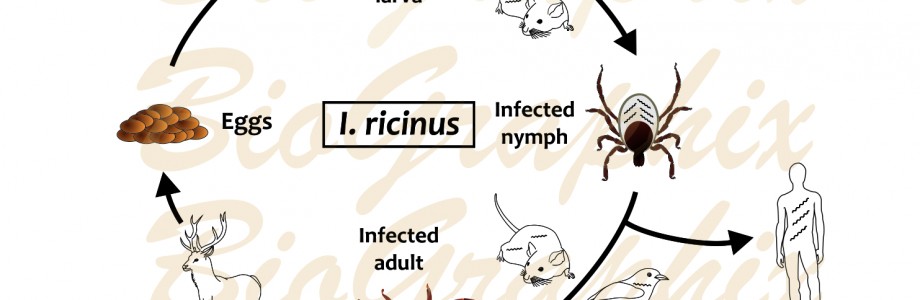
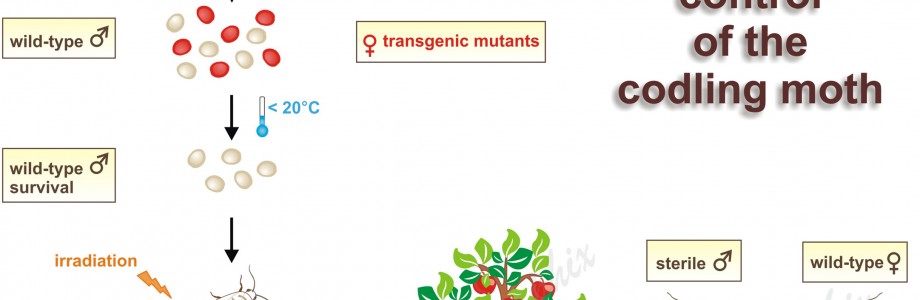
Hemoglobinolytic systems in hematophagous parasites
New illustration “Comparison of hemoglobinolytic systems in hematophagous parasites” has been recently published in the review in Trends of Parasitology. “New insights into the machinery of blood digestion by ticks. Sojka D, Franta Z, Horn M, Caffrey CR, Mareš M, Kopáček P. Trends Parasitol. 2013 Jun; 29(6):276-85. [Epub 2013 May 7].